Safety service is defined in IEC 60364-5-56 as an electrical system for electrical equipment provided to protect or warn persons in the event of a hazard, or essential to their evacuation from a location. Other standards such as IEEE refer to it as Emergency System.
Examples of safety services include:
- emergency (escape) lighting
- fire pumps
- fire rescue services lifts
- alarm systems (i.e. fire alarms, CO alarms and intruder alarms)
- evacuation systems
- smoke extraction systems
- essential medical systems.
The electrical supply system for safety services are classified as:
- non-automatic supply
- the starting of which is initiated by an operator, or
- automatic supply
- the starting of which is independent of an operator.
An automatic supply is further classified according to the maximum changeover time:
- Class A - no-break: an automatic supply which can ensure a continuous supply within specified conditions during the period of transition, for example as regards variations in voltage and frequency
- Class B - very short break: an automatic supply available within 0.15 s
- Class C - short break: an automatic supply available within 0.5 s
- Class D - average break: an automatic supply available within 5 s
- Class E - medium break: an automatic supply available within 15 s
- Class F - long break: an automatic supply available in more than 15 s.
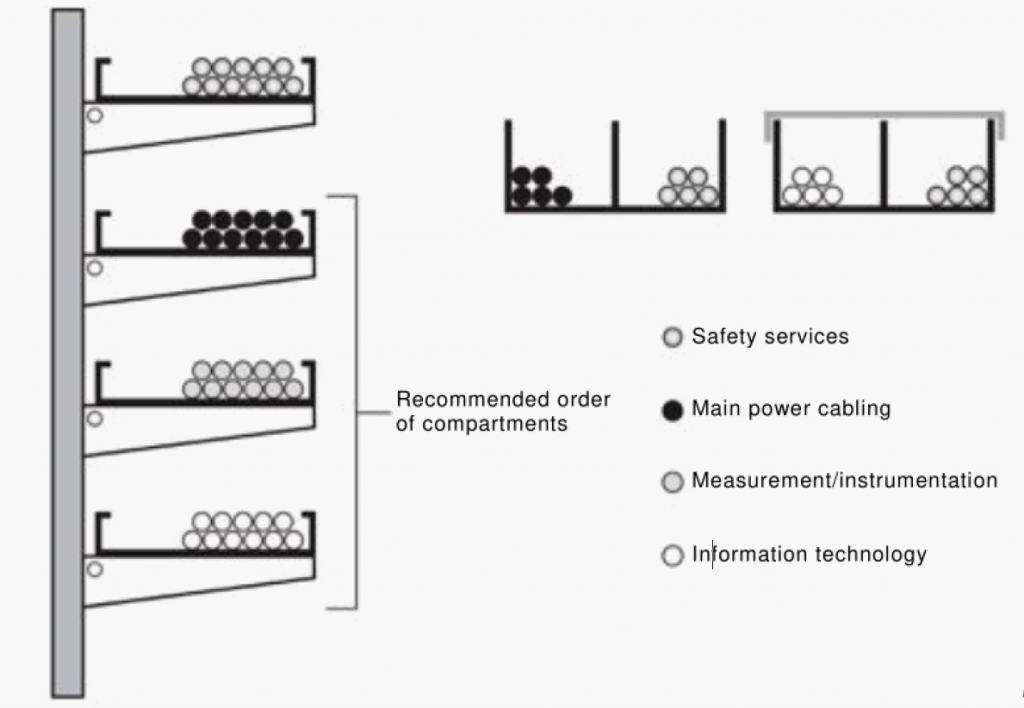
The safety services switchboard feeder circuit should be installed using a cable or conductor having fire resistance not less than for example 90 min, which is water-resistant or protected against water, and which may be connected before the fire switch. The same conditions for the feeder applies if the fire switch is installed at the building main distribution panel. All electrical sources for safety services should be segregated from any other electrical source for safety services and any other electrical source. Wiring for safety services shall be separate from the main power cabling and other services.