The impedance of a power transformer has a direct impact on the total cost of the power system. Cost of power transformer, protective devices, etc will be affected. Electrical Engineers need to be very careful in selecting the appropriate impedances of power transformers to be used in their design. International standards provide guidelines on the selection of power transformer impedances. A word of caution though, depending on the standard used in the design, recommended impedances may be typical or minimum values.
IEC 60076-5:2000 Power transformers - Part 5: Ability to withstand short circuit recommends a minimum impedance for transformers.
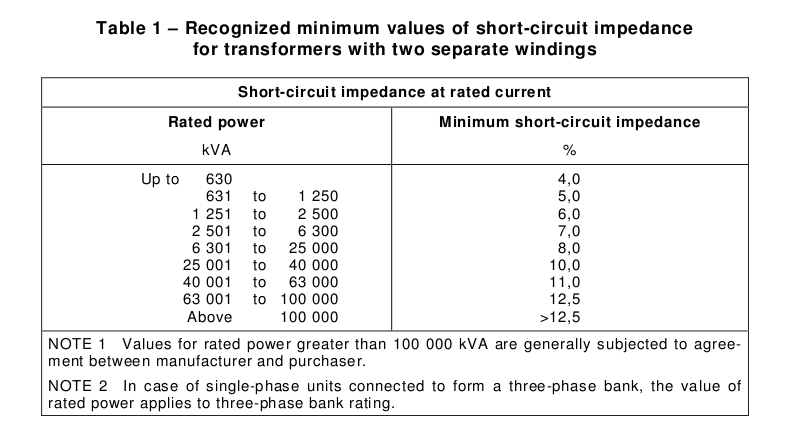
Unlike other standards such as the IEEE or Australian Standards (AS) which recommend typical values, IEC recommends minimum values. As these are minimum values, it does not mean that as an electrical designer, you can select very high impedances for your transformers. For example, IEC recommends 4%Z minimum impedance for a 300 kVA transformer. It does not mean however that you could have a 6.5%Z. Yes, you can, there will be nobody preventing you to do that but transformer %Z is directly proportional to the transformer cost, size, and weight.
Why do you have to pay more for a transformer when you can buy it cheaper b reducing the %Z? The only time you will select a higher impedance for your transformer will be to reduce the through-fault current of the transformer.
