The PEC has defined a Separately Derived System as an electrical source, other than a service, having no direct connection(s) to circuit conductors of any other electrical source other than those established by grounding and bonding connections.
Examples
Examples of separately derived systems include generators, batteries, converter windings, transformers, and solar photovoltaic systems, provided they have no direct electrical connection to another source.
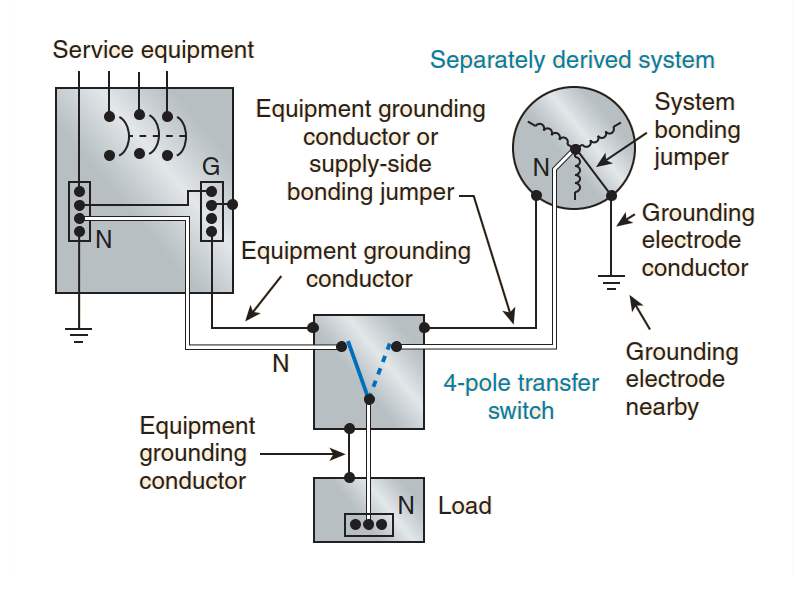
The earth, metal enclosures, metal raceways, and equipment grounding conductors may provide incidental connection between systems. In addition, 2.50.2.11(A)(6) permits a common grounding electrode conductor to be installed for multiple separately derived systems. This definition clarifies that those systems can still be considered to be separately derived systems as long as the separately derived systems have no direct electrical connection to service-derived systems. The grounded circuit con- ductors are not intended to be directly connected.
Not a Separately Derived System
An alternate ac power source, such as an on-site generator, is not a separately derived system if the grounded conductor is solidly interconnected to a service-supplied system grounded conductor. An example of such a situation is where alternate source transfer equipment does not include a switching action in the grounded conductor and allows it to remain solidly connected to the service-supplied grounded conductor when the alternate source is operational and supplying the load served.
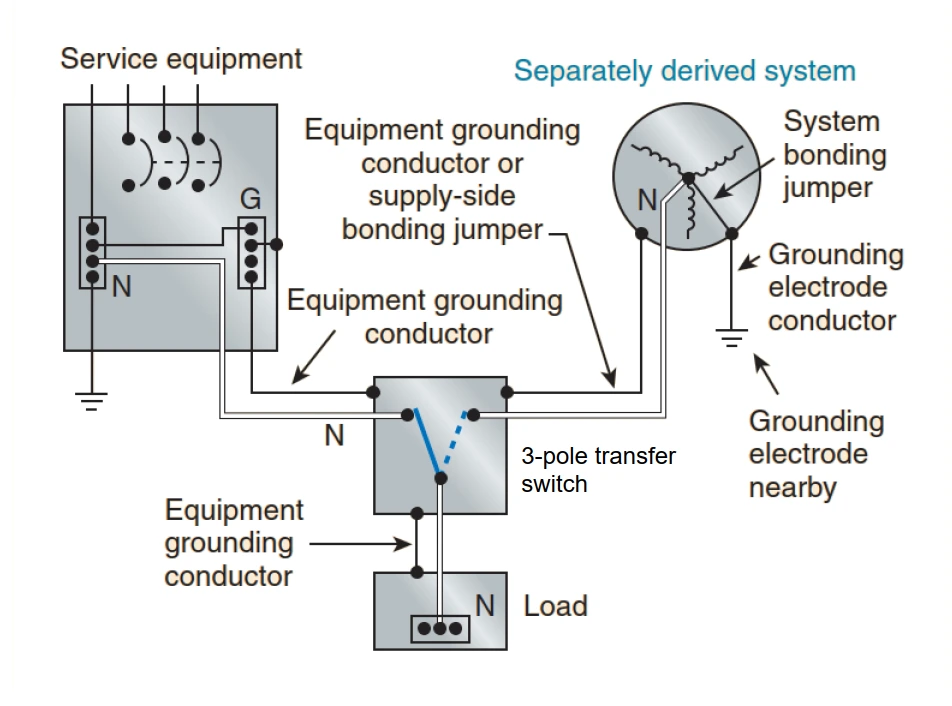
Grounding System
Section 2.50.2.11(A)(6) Grounding Electrode Conductor, Multiple Separately Derived Systems. A common grounding electrode conductor for multiple separately derived systems shall be permitted. If installed, the common grounding electrode conductor shall be used to connect the grounded conductor of the separately derived systems to the grounding electrode as specified in 2.50.2.l l(A)(4).
A grounding electrode conductor tap shall then be installed from each separately derived system to the common grounding electrode conductor. Each tap conductor shall connect the grounded conductor of the separately derived system to the common grounding electrode conductor. This connection shall be made at the same point on the separately derived system where the system bonding jumper is connected.
