Variable frequency drives (VFDs) also known as variable-speed drives or adjustable-speed drives are used to power 3-phase AC electric motors in applications requiring greater control and power efficiency. The benefits of using a VFD over traditional DC drives include more precise motor control and improved power efficiency. While there are many benefits to using VFDs, their use requires special considerations for other drive system components, in particular the VFDs output cabling.
VFDs have grown in popularity as they offer many advantages in many applications. In some applications, the correct VSD cable is also a crucial component to consider. It is important to note that many drive manufacturers do not provide enough guidance on cabling and leave this to the Design Engineer for the proper selection of the cable.
Why Use VFD Cables?
Variable frequency drives require a special type of cable that has the ability to withstand high voltage spikes in excess of the cable voltage rating under the normal operating conditions of the high-frequency application, thereby improving the operational life of the cable and the system. These voltage spikes increase with cable length, making longer cable runs more prone to premature insulation failure.
Another advantage of a VFD cable is it can prevent the generation of high levels of radiated and conducted noise during high-voltage spikes, which could interfere with the communications and with the low voltage cables in proximity to the VFD system.
These are the reasons why the use of a cable specifically designed for VFD applications is crucial to the reliability of the drive system.
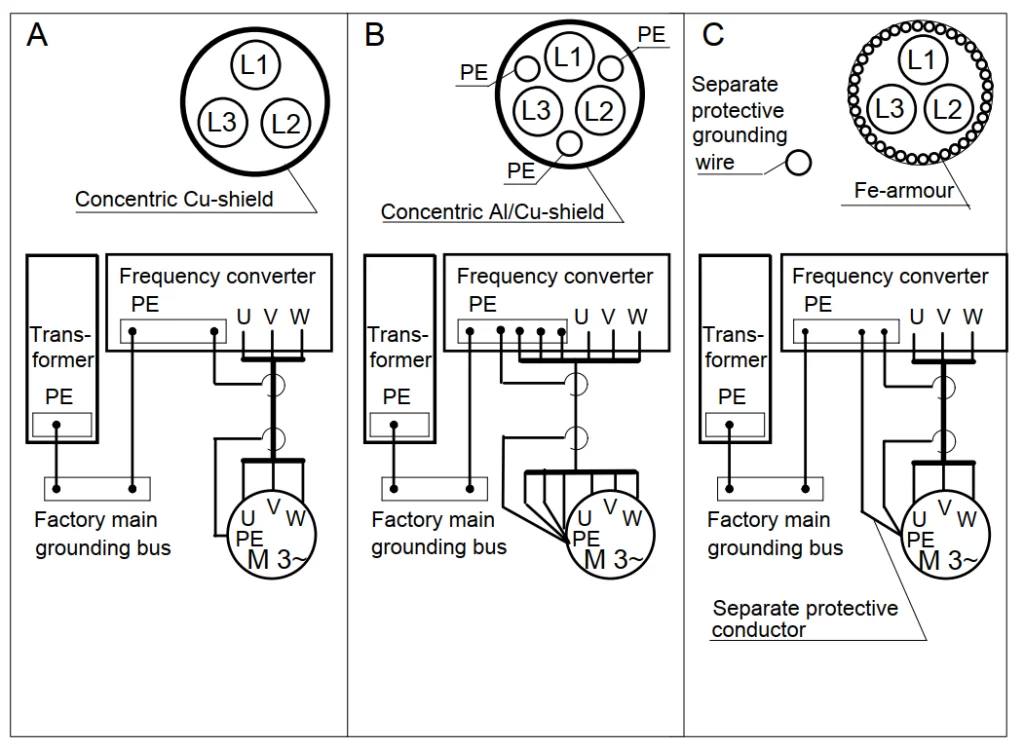
VFD Cable Types
A variety of VFD-specific cables are commercially available. These cables vary by shield type (foil/braid, copper tape, armor) and voltage level. Each voltage level directly relates to the thickness of the cable's insulation, the higher the voltage rating, the heavier the insulation, the better the cable resists high voltage spikes.
Some questions that can help in the VFD cable selection are:
- Is physical protection required for the cable?
- Is the cable exposed to physical harm under normal operating conditions?
- Is the cable run more than 50 meters?
- Is the cable routing near any low-voltage or communications cables?
- Is the cable need to be flexible or easy to install?