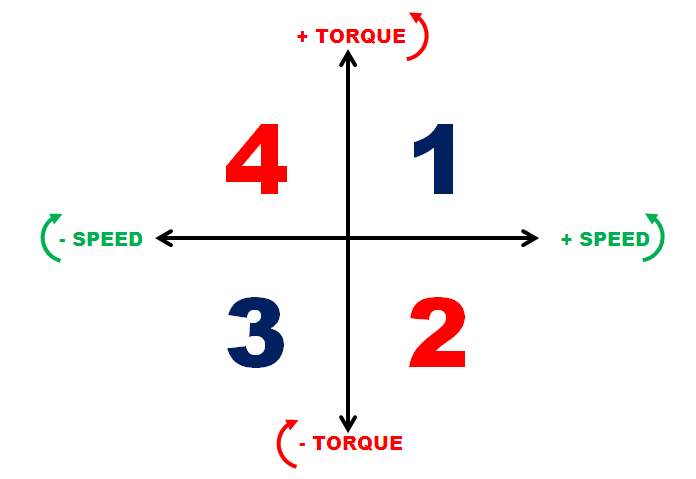
Variable speed drives are capable of operating in 4-quadrant modes of operation. When energy is transferred from the electric motor to the mechanical load, it is operating in motoring mode. These modes take place in quadrant 1 and 3. If energy is transferred from the mechanical load to the electric motor, it is operating in generating or braking mode.
- Quadrant 1
- Torque is positive and speed is positive.
- Power is positive, energy is transferred from the electric motor to the mechanical load.
- Mechanical load is rotating in the forward direction.
- Quadrant 2
- Torque is negative and speed is positive.
- Power is negative, energy is transferred from the mechanical load to the electric motor. In some types of variable speed drives this energy can be transferred back into the electrical power source. This is called regenerative braking.
- Mechanical load is rotating in the forward direction.
- Quadrant 3
- Torque is negative and speed is negative.
- Power is positive , energy is transferred from the electric motor to the mechanical load.
- Mechanical load is rotating in the reverse direction.
- Quadrant 4
- Torque is positive and speed is negative.
- Power is negative, energy is transferred from the mechanical load to the electric motor. As in Quadrant 2, some types of variable speed drives this energy can be transferred back into the electrical power source. This is called regenerative braking.
- Mechanical load is rotating in the reverse direction.
It should be noted that, an electric motor always puts out a torque in a direction so as to cause the rotor to approach synchronous speed of the rotating air-gap magnetic field.
- In the motoring mode, the inverter output frequency will always be higher than the rotor speed.
- In the generating (braking) mode, the inverter output frequency will be at a frequency lower than the rotor speed. The braking torque produced during deceleration is dependent on the slip in the motor.
Current-source inverters (CSI) are capable of regenerative braking without modification and other braking techniques need not be considered.
Voltage-source inverters (VSI), which include Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) types, cannot regenerate without costly modifications to the rectifier module.