Whenever the voltage at the terminals of an induction motor varies from its nameplate rating, either performance or life is sacrificed.The effect may be minor or serious depending upon the characteristics of the induction motor. , how it is applied and the amount of the voltage deviation from the motor rating. Standards provide certain tolerances within which equipment will operate without seriously affecting performance. However, there is always a major sacrifice in performance for voltage variations of considerably less than those given in the equipment rating.
General Effect of Voltage on Induction Motor Characteristics
| Characteristics | Voltage Variation | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Function of Voltage | 90 Percent Voltage | 110 Percent Voltage | |
| Starting and Maximum Running Torque | (Voltage)2 | Decreases 19% | Increases 21% |
| Synchronous Speed | Constant | No Change | No Change |
| Percent Slip | 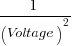 |
Increase 23% | Decrease 17% |
| Full Load Speed | (Synchronous Speed - Slip) | Decrease 1-1/2% | Increase 1% |
| Efficiency | |||
| Full Load | - | Decrease 2% | Increase 1/2 to 1% |
| 3/4 Load | - | Practically no change | Practically no change |
| 1/2 Load | - | Increase 1 to 2% | Deacrease 1 to 2% |
| Power Factor | |||
| Full Load | - | Increase 1% | Decrease 3% |
| 3/4 Load | - | Increase 2 to 3% | Decrease 4% |
| 1/2 Load | - | Increase 4 to 5% | Deacrease 5 to 6% |
| Full Load Current | - | Increase 11% | Decrease 7% |
| Starting Current | Voltage | Decrease 10 to 12% | Increase 10 to 12% |
| Temperature Rise, Full Load | - | INcrease 6 to 7% | Decrease 1 to 2% |
| Maximum Overload Capacity | (Voltage)2 | Decrease 19% | Increase 21% |
| Magnetic Noise at No Load | - | Decrease Slightly | Increase Slightly |
