Note: This is will be part 2 of the selection of power circuit breaker rating series. Part 1 could be found here.
Voltage Rating
Selecting the correct voltage rating of a power circuit breaker is very important. This will insure that the power circuit breaker will function the way it is expected to be. There are several parameters to be considered in voltage selection. These are enumerated and briefly explained below:
- Rated kV
- The nominal vltage class or classes in which the circuit breaker is rated.
- Maximum Design kV
- The maximum voltage at which the circuit breaker is designated to operate.
- The upper limit of the highest voltage of systems for which the circuit breaker is intended to operate.
- Minimum Operating kV
- The minimum voltage at which the circuit breaker will interrurpt its rated MVA. At any voltages below this vlaues, the circuit breaker is required to be derated to a value less than than the rated MVA.
- This is a very significant rating of power circuit breakers as the circuit breaker will interrupt a maximum current regardless of the voltage.
- At any voltage less that the minimum operating voltage, the product of the maximum KVA interrupting rating times kV times the square root of 3 is less than the MVA interrupting rating of the circuit breaker. This is mathematically represented below formula
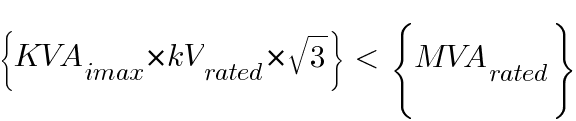
where:
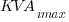 = maximum KVA interrupting rating
= maximum KVA interrupting rating
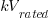 = kV rating
= kV rating
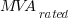 = MVA rating
= MVA rating
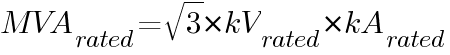
where:
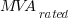 = rated MVA interrupting rating
= rated MVA interrupting rating
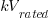 = kV rating
= kV rating
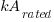 = rated interrupting current
= rated interrupting current
