Philippine Electrical Code 2017 Part 1/Chapter 1. General/Article 1.3 - Electrical Plans And Specifications
Article 1.3 - Electrical Plans And Specifications
While the authors have used good faith and efforts to ensure that the information and instructions contained in this work are accurate, the authors disclaim all responsibility for errors or omissions, including without limitation responsibility for damages resulting from the use of or reliance on this work. Use of the information and instructions contained in this work is at your own risk. If any contents or other technology this work contains or describes is subject to open source licenses or the intellectual property rights of others, it is your responsibility to ensure that your use thereof complies with such licenses and/or rights.
Note: This is a work in progress...
1.3.1 General
1.3.1.1 Drawing Sheet Sizes.
(A) Electrical plans and drawings shall be drawn on drawing sheets of the following standard sizes:
- 760 mm x 1 000 mm
- 600 mm x 900 mm
- 500 mm x 760 mm
(B) In cases such as projects of large magnitude, an exemption in the use of the standard drawing sheets may be granted by the office of the local building official.
(C) For a dwelling unit having a floor area of not more than 50 square meters with a total load not exceeding 3 680 VA, a drawing sheet of size 297 mm x 420 mm (A3 size) is permitted.
With the advent of computer-aided design, drawing sizes may change. The common practice now internationally is to use A3 for any drawing.
1.3.1.2 Drawing Scale.
Appropriate metric drawing scales shall be used.
1.3.1.3. Graphic Scale.
Since the size of the drawing sheet can be changed photographically, graphic scale shall be shown on each drawing sheet.
FPN: Graphic scale denotes nominal or average plan scale and remains true when plans are photographically reduced.
1.3.2 Plans and Specifications
1.3.2.1 Plan Requirements.
(A) Location and Site Plans.
Location and site plans, with proposed e. Others structure and owner’s land drawn to appropriate metric scale shall show:
- (1) Bordering areas showing public or well-known streets, landmarks and/or structures which need not be drawn to scale unless they extend into the area concerned;
- (2) Location of service drop, service equipment and nearest pole of the utility company furnishing electrical energy; location of the meter as well as sizes of service entrance wires, conduits and service equipment; and
- (3) Clearance of the path or run of service drops and entrance wires to adjacent existing and/or proposed structures.
(B) Legend or Symbols.
Refer to Appendix A – Electrical Symbols
(C) General Notes and/or Specifications.
General Notes and/or Specifications, written on the plans or submitted on separate standard size sheets shall show:
- (1) Nature of electrical service, including number of phases, number of wires, voltage and frequency;
- (2) Type of wiring;
- a. Service entrance
- b. Feeders, sub-feeders and branch circuit wires for lighting and/or power load
- c. Fire alarm system, if required by law
- d. Signaling and communication
- (3) Special equipment to be installed, indicating ratings and classification of service or duty cycle of;
- a. Rectifiers
- b. Heaters
- c. X-ray apparatus
- d. Electric welding equipment
- e. Others
- (4) System or method of grounding;
- (5) Type and rating of main disconnecting means, overcurrent protection (OCP) and branch circuit wiring;
- (6) Clearances of service drop, burial depth for service lateral, mounting height and clearance for service equipment, mounting height and clearance for kWh meter.
(D) Electrical Layout.
Floor plan showing the location of equipment and devices, and their interconnection wiring.
(1) Plan for Power.
Layout and wiring plans for power on the floor plans drawn to scale, shall show:
- a. Sizes and location of service entrance conductors, raceways, metering equipment, main switchboard, layout of feeders and distribution panels or switches and their sizes, types, and ratings;
- b. Complete circuits of motors and other electrical equipment, their controlling devices, their locations, and ratings;
- c. Complete wiring of emergency power system, if any;
- d. Nature of processes/activities carried out in each room or area
FPN: In residences, apartment houses, and small commercial establishments, layout of equipment and motors of one horsepower or less may be incorporated in the layout for General Lighting and Receptacle Outlets. In general, layout of motors and power outlets not exceeding a total of ten, may be included in the lighting layout provided such inclusion will not make reading, interpretation and/or checking of said plan difficult.
(2) Plan for Lighting and Receptacle Loads.
Layout and wiring plans for general lighting and receptacle outlets on floor plans drawn to scale, shall show:
- a. Location, type and rating of lighting fixtures, indicating illumination in lux in each room or area. In residences, hotels, apartment houses, and churches, the illumination level in each room or area need not be shown nor computed;
- b. Location of switches for each fixtures or group of fixtures;
- c. Location of receptacle outlets and appliances to be served and their ratings;
- d. Complete circuits of the lighting and receptacle outlets;
- e. Complete wiring of emergency lighting system, if any;
- f. A separate drawing showing layout of receptacle outlets may be made at the discretion of the design engineer.
(3) Plan for Fire Alarm Circuits.
Layout and wiring plans of fire alarm station, fire alarm bell, fire alarm control panel, and others shall be drawn to scale and show:
- a. Location of outlets, equipment and/or apparatus and controls;
- b. Complete circuit showing no. and size of raceway and wire;
(E) Schedule of Loads.
Schedule of load in tabulated form shall indicate:
(1) Motor Loads;
- a. Motors as numbered or identified in power layout
- b. Type of motor
- c. Horsepower/kilowatt/kilovolt ampere rating
- d. Voltage rating
- e. Full-load current rating
- f. Frequency rating other than 60 hertz
- g. Number of phases
- h. Type and size of wiring
- i. Protective device rating
(2) Lighting and Receptacle Loads;
- a. Panel as numbered in the feeder diagram
- b. Circuit designation number
- c. Number of lighting outlets in each circuit
- d. Number of switches in each circuit
- e. Number of receptacles outlets (convenience outlets)
- f. Voltage of circuit
- g. Type and size of wiring
- h. Protective device rating
(3) Other Loads.
- a. Designation number on plan
- b. Description of load
- c. Classification of service duty, if required
- d. Rating of kilovolt-ampere or kilowatt
- e. Phase loading indicating full load line current
- f. Voltage rating
- g. Type and size of wiring
- h. Protective device rating
(F) Design Analysis.
Design analysis shall be included on the drawings or shall be submitted on separate sheets of standard size, and shall show:
- (1) Branch circuits, sub-feeders, feeders, busways, and service entrance;
- (2) Types, ratings, and trip settings of overload protective devices;
- (3) Calculation of voltage drops.
- (4) Calculation of short circuit current for determining the interrupting capacity of overcurrent protection device for residential, commercial, and industrial establishment;
- (5) Protection coordination of overcurrent protective devices;
- (6) Arc-flash Hazard Analysis to determine the required personal protective equipment (PPE) in other than dwelling place - (see Appendix H for PPE)
FPN No 1: This analysis is not required for dwelling units but required for service equipment and other electrical equipment not part of the individual dwellings units of residential condominiums and individual detached dwelling units.
FPN No. 2: Arch-flash hazard analysis required is intended for concerned parties to be informed and made aware of the importance of personal protective equipment (PPE) and its type for the flash hazard risk category determined by the analysis. Further overcurrent protective coordination coupled with the flash hazard analysis can reduce the severity of PPE needed but is not required under this arc-flash hazard analysis.
FPN No. 3: IEEE Std 1584-2002, Guide for Performing Arc-Flash Hazard Calculations provides guidelines for arc-flash hazard analysis.
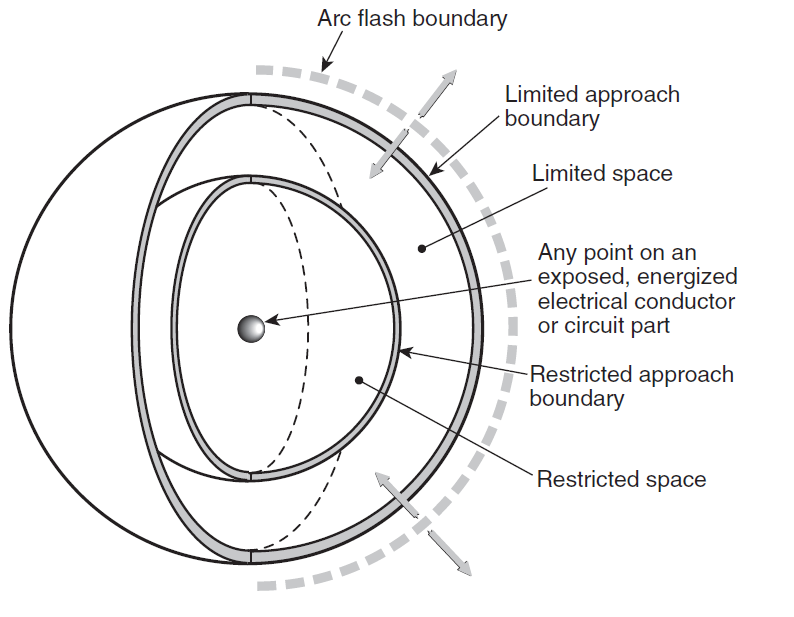
NFPA 70E Standard for Electrical Safety in the Workplace provides guidelines for a practical safe working area for employees relative to the hazards arising from the use of electricity. It also provides guidelines on the selection of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) required for various tasks.
NFPA 70E also provides "Limits of Approach" to an exposed energized conductor.
(G) One Line Diagram.
One line diagram shall indicate:
(1) Lighting and Receptacle Outlet Loads;
- a. Single line or schematics diagram of lighting and receptacles panelboards showing mains and branch circuit rating;
- b. Size of conductors for feeders.
(2) Motor Loads;
- a. Rating in kilowatts/horsepower/kilovolt ampere
- b. Full load current
- c. Locked rotor current
- d. Phase connection for 1-phase motor on a 3-phase system
- e. Rated voltage
- f. Type and size of wiring, indicating load in amperes
- g. Electric motors shall be numbered consecutively to correspond to their numbers in the layout
(3) Feeders and Subfeeders;
- a. Identification and/or labeling of feeders and subfeeders
- b. Size and type of wires and raceway
- c. Protective devices and controls
- d. The allowable ampacity of the conductor over the designed load current in amperes expressed as a ratio and indicated alongside the conductor
(4) Load Center.
- a. Identification and/or labeling of load center showing type and rating of transformer, switches, circuit breaker and other related devices
- b. Incoming and outgoing feeders, type, size and voltage
- c. Equipment grounding
1.3.2.2 Title Block.
Title block or nameplate of plans and drawing shall be a standard strip of 40 mm high at the bottom of the sheet.
It shall contain the following:
- (A) Name and location of installation or project;
- (B) Name, signature and address of owner/manager/operator;
- (C) Title of sheet;
- (D) Name, signature, and seal of Professional Electrical Engineer together with Professional Regulation Commission professional license number and validity, Professional Tax Receipt Number, and Tax Identification Number;
- (E) Scale used, date drawn; and
- (F) Sheet number.
1.3.2.3 Other Details.
(A) Exposed conductors shall show:
- (1) Means of support and types of insulators; and
- (2) Spacings and clearances.
(B) Auxiliary gutters, wireways, busways, cabinets, boxes, metallic raceways, underground installations, other than specified in the Code shall show:
- (1) Installation details;
- (2) Conductor supports, separators, and attachments where required by this Code; and
- (3) Dimensions and description or specifications.
(C) Private pole installations shall show:
- (1) Construction and installation details and dimensions;
- (2) Pole top wiring details including line hardware; and
- (3) Guying details.
(D) Low energy power and low voltage power installation shall show:
- (1) Details of battery installation and/or other sources of low voltage or low energy power;
- (2) Equipment, wiring, actuating mechanism and protective devices; and
- (3) Ventilation details whenever necessary.
1.3.3 Substation Plans and Specifications
1.3.3.1 Indoor Substation.
Indoor substation plans shall show:
(A) Location and dimensions of;
- (1) Substation in building plan drawn to scale,
- (2) Building with respect to entire compound or property,
- (3) Incoming and outgoing lines, and
- (4) Windows, doors, and other openings.
(B) Substation structural requirements;
- (1) Materials and construction of walls, floors, roof, windows, enclosures, doors, and their dimensions, and
- (2) Ventilation and drainage systems and other safeguards.
(C) Substation electrical requirements such as;
- (1) Plan view showing location and sizes of equipment installed,
- (2) Clearances and spacings between exposed current-carrying and noncurrent-carrying portions and grounding equipment, and
- (3) Grounding system.
(D) Cross sectional views showing;
- (1) Horizontal and vertical clearances between exposed parts and adjacent surfaces,
- (2) Horizontal and vertical clearances of exposed parts from floor/ceiling,
- (3) Finished floor level and ground level.
(E) Miscellaneous;
- (1) Specification of equipment,
- (2) Wiring of lighting and remote control systems,
- (3) One-line diagram(s) of entire installation with voltage indicated,
- (4) Computations on size of wires, busbar, transformer, fuses, switches and breaker, and
- (5) Class of insulation or insulators.
1.3.3.2 Outdoor Substation.
Outdoor substation plans shall show the same items as indoor substations except that in lieu of walls and roof, details of fence and supporting steel structure shall be shown in accordance with the latest edition of the Philippine Electrical Code, Part 2.
Other Pages in this Category: Chapter 1. General
<DynamicPageList> category = Philippine Electrical Code 2017 Part 1/Chapter 1. General count = 5 order = ascending addfirstcategorydate = false </DynamicPageList>